Why Study at EIIET? Unveiling the Benefits of a Private Institute in Germany
June 20, 2024
The Ultimate Guide to Studying Tourism and Recreation in Germany
July 12, 2024Things To Know Before Studying in Germany: A Comprehensive Guide
Germany is one of the most preferred destinations among international students. There are several reasons why students want to make Germany their preferred educational destination. German universities are known for their high standards, which enable students to make valuable connections, broaden their knowledge, and hone their talents in preparation for their desired careers from an early age. These are only a few things to know before studying in Germany.
In addition, students can engage in many activities while in Germany, such as touring historical sites, going on nature walks, and trying the regional cuisine. However, you should know several important things before you pack your bags. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know before your study journey in Germany.
1. Understand the German Education System
1.1 Types of Institutions
Germany offers various types of higher education institutions. These include Universities, Universities of Applied Sciences, Colleges and Institutes. Universities focus more on theoretical knowledge, while universities of applied sciences emphasise practical skills. Colleges and private institutes cater to students interested in creative disciplines.
1.2 Degree Programmes
Germany follows the Bologna Process, which standardised higher education across Europe. This means you can pursue bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees. Bachelor's programmes usually span three to four years, and postgraduate programmes generally last three to five years. You can even study English abroad in Germany.
1.3 Language of Instruction
Numerous programmes are available in German, yet an expanding array of courses are now offered in English across all levels. Please review the language requirements for your chosen programme and confirm that you meet them. If your programme is taught in German, you might be required to pass a language proficiency exam such as TestDaF or DSH.
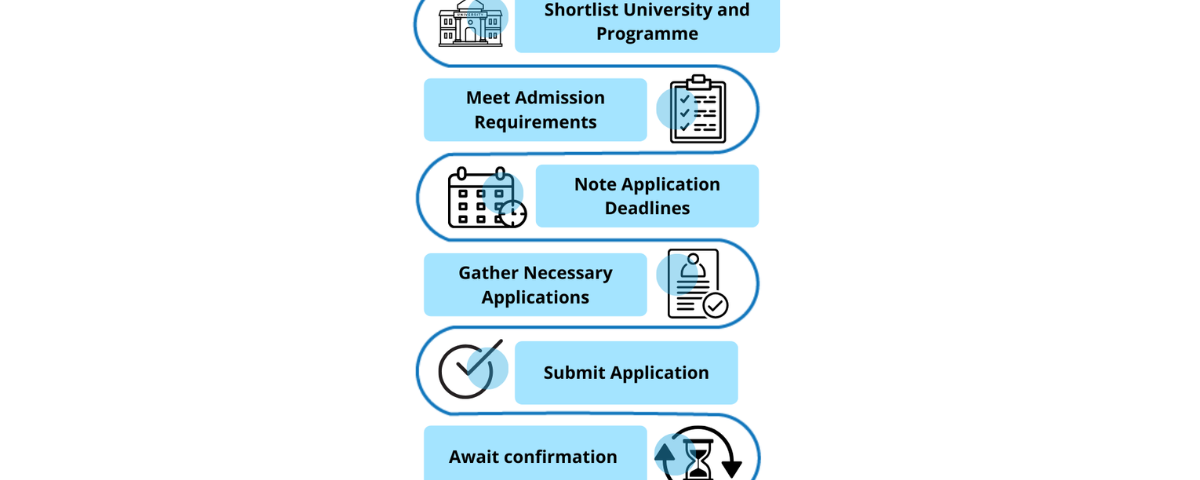
2. Application Process
2.1 Choosing the Right University and Programme
Conducting thorough research is essential. Utilise resources such as DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service) to discover programmes that align with your interests and qualifications. Consider the university's reputation, location, and the cost of living in the area.
EIIET can be one of your options if you are looking for undergraduate and postgraduate degrees in Hospitality, Tourism, and Recreation.
2.2 Meeting Admission Requirements
Admission requirements vary by institution and programme. Generally, you'll need a recognised secondary school diploma, proof of language proficiency, and sometimes a pre-university qualification or entrance exam. For master's programmes, a relevant bachelor's degree is required.
2.3 Application Deadlines
Application deadlines in Germany can be strict. Winter semester deadlines usually fall between May and July, while summer semester deadlines are between December and January. Always check the specific dates for each institution.
2.4 Preparing Your Documents
Gather your academic transcripts, proof of language proficiency, a CV, a letter of motivation, and letters of recommendation as part of your application preparation. Some programmes may also require a portfolio or evidence of work experience.

3. Financial Preparation
3.1 Tuition Fees
Germany is well-known for its reasonably priced tuition fees, which draw students from all over the world. The cost of education in Germany is relatively low compared to many other countries, enabling students to obtain a high-quality education without facing substantial financial strain.
3.2 Cost of Living
The cost of living in Germany varies by city. You will need around €850 to €1,200 per month. This budget covers rent, food, health insurance, transport, phone/internet, study materials, and leisure activities.
3.3 Scholarships and Financial Aid
There are numerous scholarships available for international students studying in Germany. Organisations like DAAD, Erasmus+, and various foundations offer financial aid. Do some research on such opportunities carefully, then apply.
4. Visa and Residence Permit
4.1 Student Visa
For academic purposes in Germany, non-EU students require a student visa. Apply for this visa at your home country's German embassy or consulate. You will need your university admission letter, proof of financial resources, health insurance, and a valid passport.
4.2 Residence Permit
Once in Germany, you must go to your community's Foreigners' Registration Office and apply for a residence permit. You will need your visa, proof of accommodation, health insurance, and a biometric photo. With this permit, you can remain in Germany for the entire duration of your studies.
5. Health Insurance
Health insurance is mandatory in Germany. There are two types of health insurance available: private and public. Most students opt for public health insurance, which costs around €120 - €130 monthly. Ensure you have coverage before enrolling at your university.
6. Accommodation
6.1 Types of Accommodation
You can live in student dormitories, private apartments, or shared flats (WG). Dormitories are affordable but in high demand. Private apartments offer more independence but are costlier. Shared flats are a popular and budget-friendly option.
6.2 Finding Accommodation
Start looking for accommodation early. Websites like Studentenwerk and WG-Gesucht can help you find the accommodation of your choice. University housing offices may also assist international students.
7. Cultural Adaptation
7.1 Language
Learning German will significantly enhance your experience. Even if your course is in English, knowing German will help you in daily life and improve your job prospects.
7.2 Social Etiquette
Germans value punctuality, privacy, and direct communication. Be on time for appointments, respect personal space, and expect honest feedback.
7.3 Making Friends
While in Germany, do not hesitate to join student clubs, attend university events, and participate in cultural activities to meet new people. International offices often organise orientation programmes to help new students settle in.
8. Working While Studying
8.1 Part-time Jobs
Students from outside the EU are permitted to work up to 120 full days or 240 half days each year. Typical student jobs include tutoring, working in coffee shops, and doing internships in your subject of study.
8.2 Internships
One excellent approach to obtaining real-world experience is through internships. Many degree programmes include mandatory internships. Be aware of the work regulations and seek opportunities that complement your studies.
9. Cultural Adjustment
9.1 Language and Communication
Even if you are enrolled in an English-taught programme, learning German will significantly enhance your experience. It will help with everyday tasks and make socialising easier.
9.2 Social Integration
Join student clubs and organisations to meet new people and integrate into German society. Experiencing the local culture can be significantly enhanced by attending cultural events and festivals.
9.3 Understanding German Etiquette
It would help if you learned to be polite before stepping into Germany. Germans follow regulations, are clear communicators, and are prompt. Gaining an understanding of these cultural differences will facilitate your adjustment.
10. Preparing for Departure
10.1 Packing Essentials
Pack appropriate clothing for the weather, as Germany experiences all four seasons. Remember important documents, medications, and any electronics you might need.
10.2 Arrival Preparation
Have a plan for your arrival, including transportation from the airport and temporary accommodation if necessary. Make sure to have some euros on hand for initial expenses.